Create Anaglyph Images With Your Camera
Capture two photos of a scene with a slight horizontal shift in camera position to create an anaglyph image. The anaglyph image can then be viewed using special glasses with lenses that filter red and cyan colors to produce a 3D visualization of the scene.
Index
Stereoscopic Vision and Depth Perception
Stereoscopic Vision and Depth Perception
Each of your eyes sees a slightly different view because they are spaced apart horizontally. An object that is common to both the left and right view will appear horizontally shifted relative to the other.
The relative horizontal difference between the common objects is called disparity. Close objects have a larger disparity than far away objects. It is this correspondence that the brain uses to perceive distance.
Verify this by looking at a close and distant object alternately with the left and right eye. The closer the object is to the eyes the more it appears to shift in position between the left and right view.
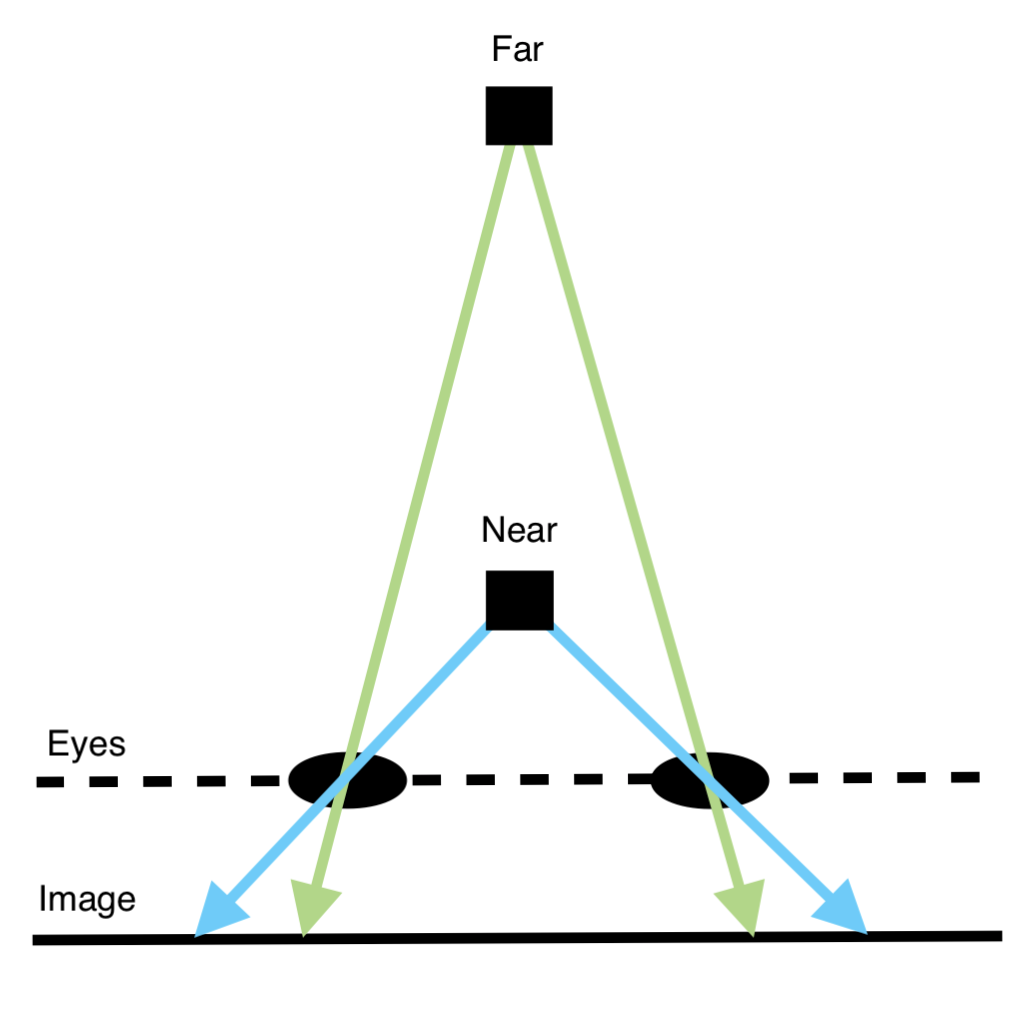
Imaging Near and Far Objects
Tracing rays of light from object to image plane through eyes.
|
Color and RGB Channels
RGB stands for the red (r), green (g), and blue (b) pure colors used to create a larger set of colors in a digital image. A digital image is a rectangular array of pixels. Each pixel is assigned three values (r,g,b) specifying the intensity of pure red, green and blue. The (r,g,b) 3-tuple are quantized values of the intensity, in a range of integers from maximum intensity, say 255, to none, or 0.
In this way a full color digital image can be decomposed into three other digital images, or channels, one for each color component. The red channel pixels have values that are the red value of the corresponding pixels in the given image. Similarly for green and blue.
Example 1: rgb = (255, 0, 0) means the pixel is pure red, no green or blue.
Example 2: rgb = (0, 255, 255) creates pure cyan by mixing only green and blue at full intensity.
Example 2 is important: namely that cyan = green + blue. Therefore decomposing an image into red, green and blue channels can be used to decompose an image into red and cyan channels, by combining the green and blue channels into one. This is important for generating an anaglyph in the next section.
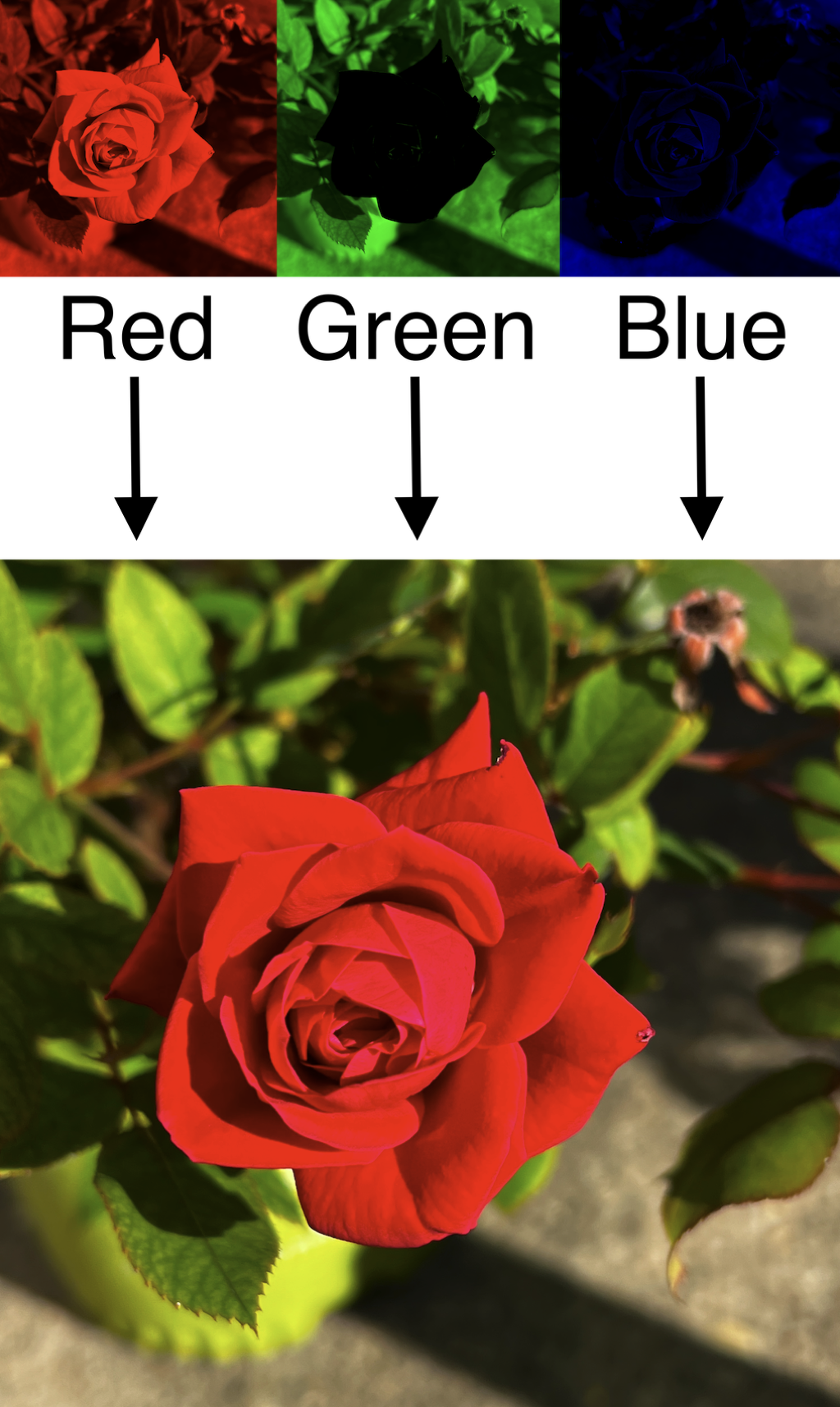
Full Color Image
Decomposed into red, green and blue channels.
|
RGB Color Mixer
Experiment with these sliders to see how adjusting each color channel affects the overall color. The combination of red, green, and blue channels determines the color displayed on the screen.
Hex: #FF0000
RGB: (255, 0, 0)
Anaglyph Image Composition
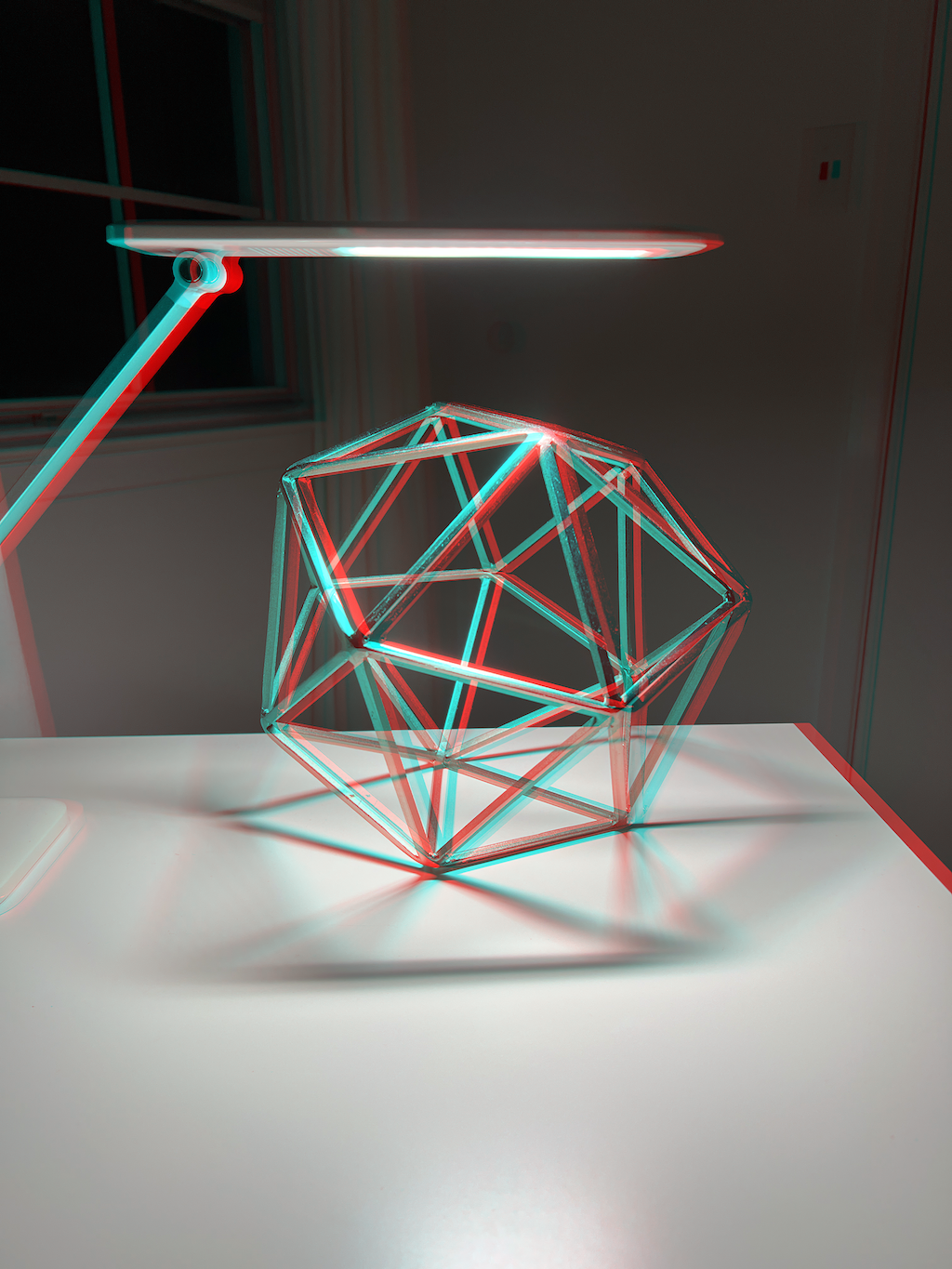
An anaglyph image is a way to encode the disparity between two images into one. So it is an image made from two other images — one for the left eye and one for the right eye — to simulate 3D viewing with special glasses. An anaglyph is created using RGB channels extracted from a given image pair using the following procedure.
A full color image can be decomposed into its RBG channels. This decomposition is performed for each of the left and right images. Conversely an image can be constructed from RGB channels. In this case an anaglyph image is generated by setting its red channel to the red channel of the left image, and its green and blue channels to those of the right image. As noted previously cyan = green + blue, so an anaglyph can be thought of as the composition of a red and cyan channel, taken from the left and right images respectively.
In this way the anaglyph image is a color image that has encoded the depth information from disparity between the left and right images, being composed of channels of both. Moreover it shares color information. Although it does not preserve color fidelity, it presents colors that are similar to the originals.
The similarity of colors is exhibited here, where the left eye images are compared to their anaglyphs.

Left Eye
|
Anaglyph
|
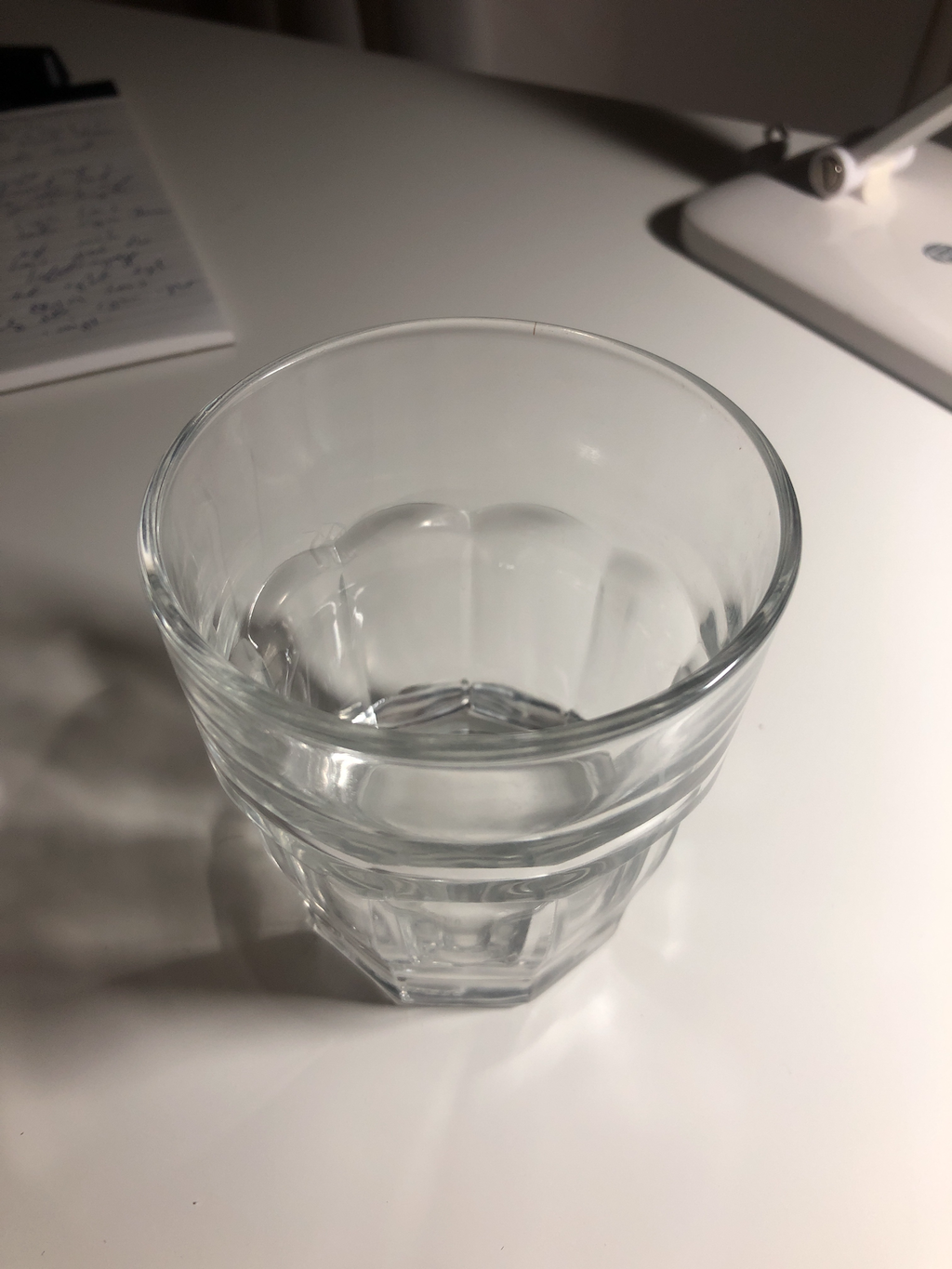

Left Eye
|
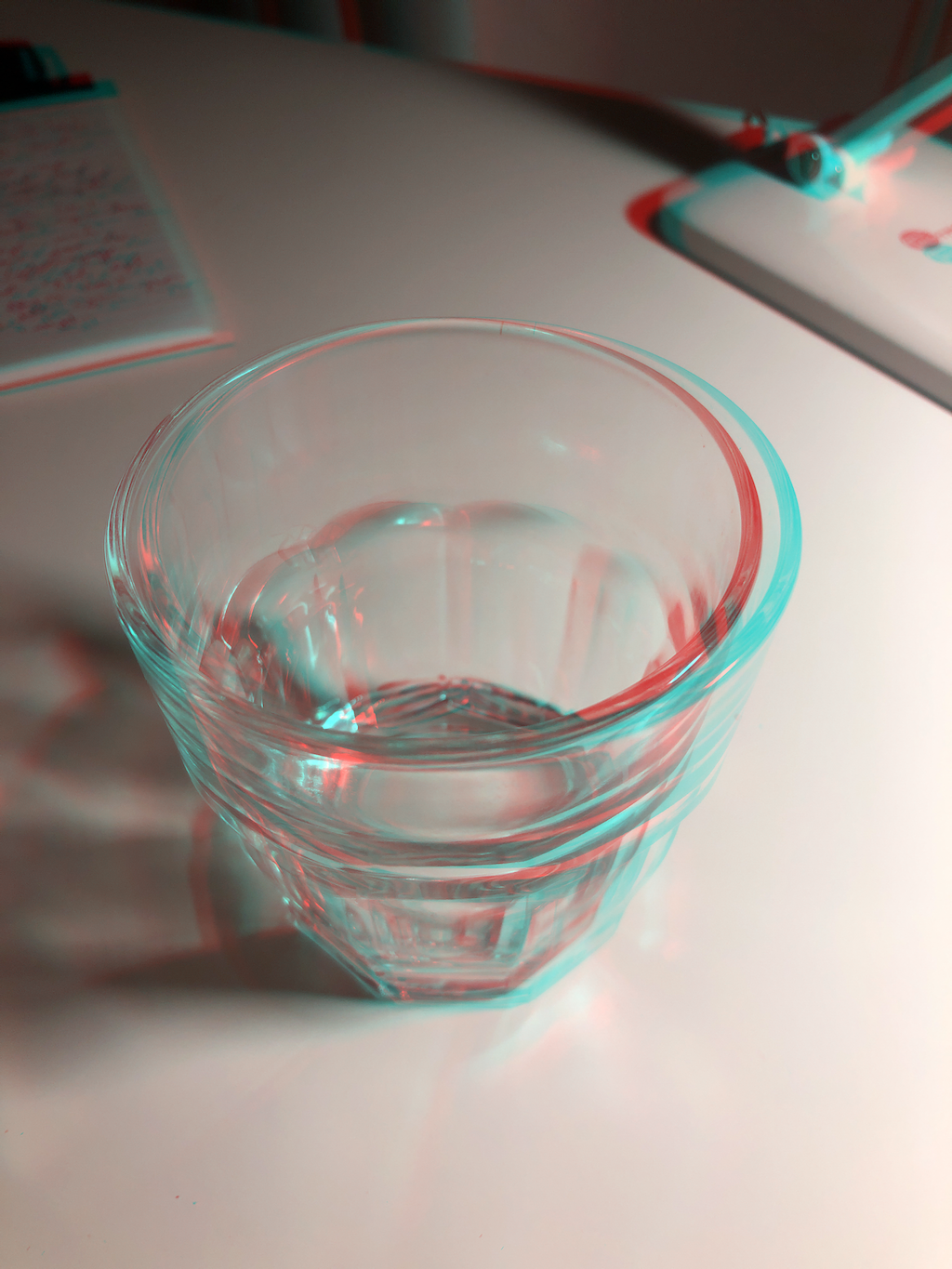

Anaglyph
|

Left Eye
|
Anaglyph
|
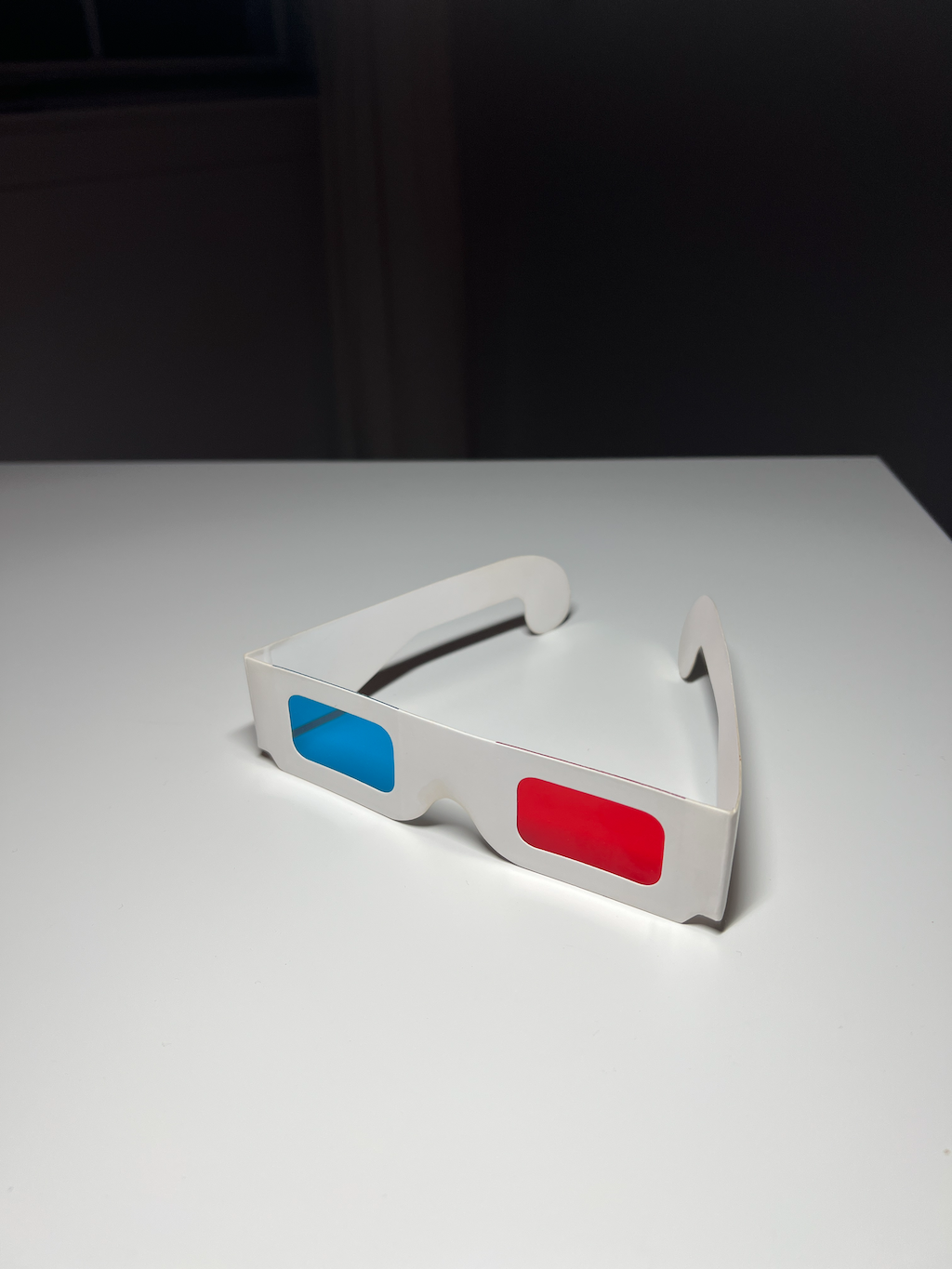
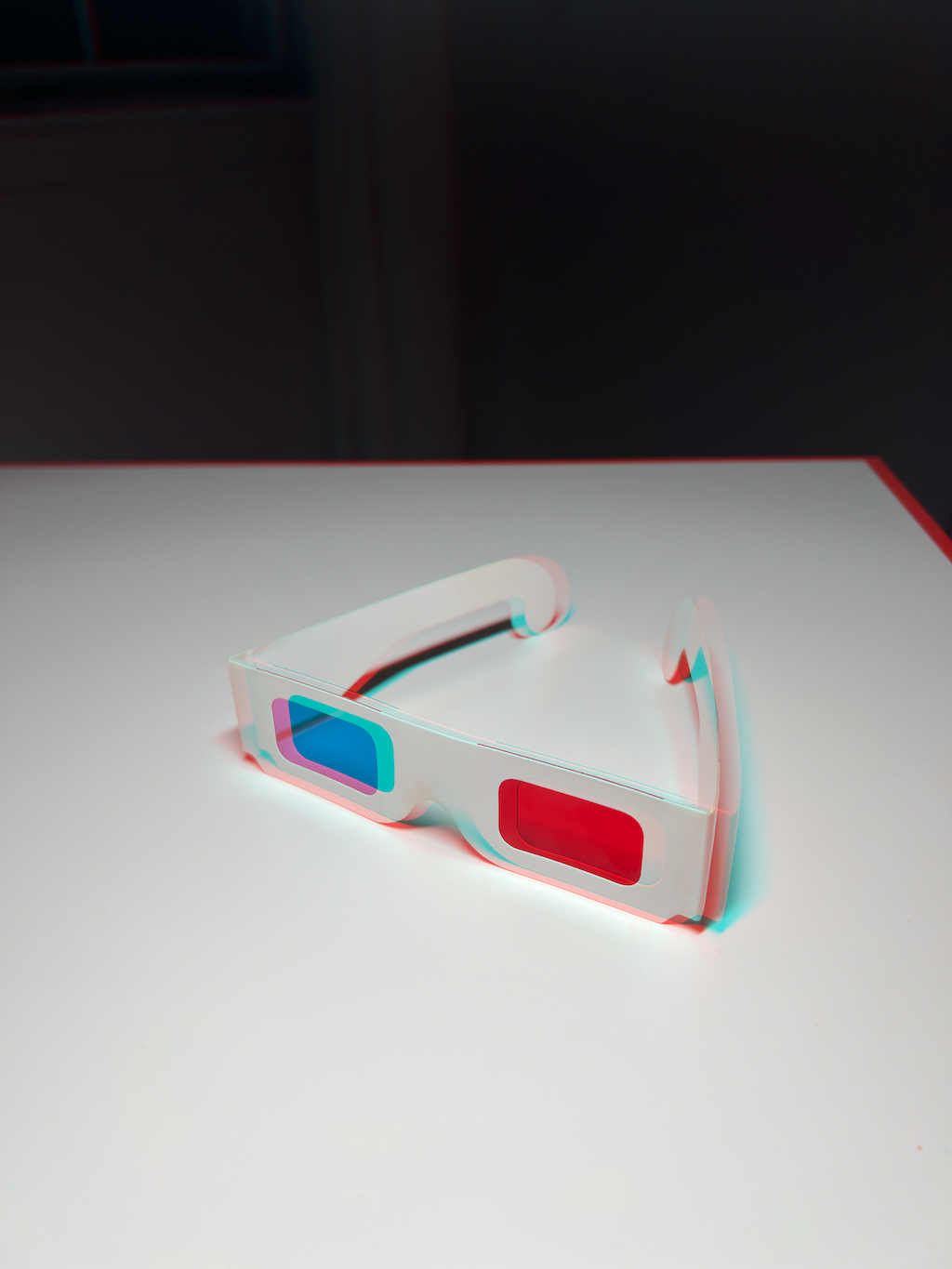
How 3D Glasses Work
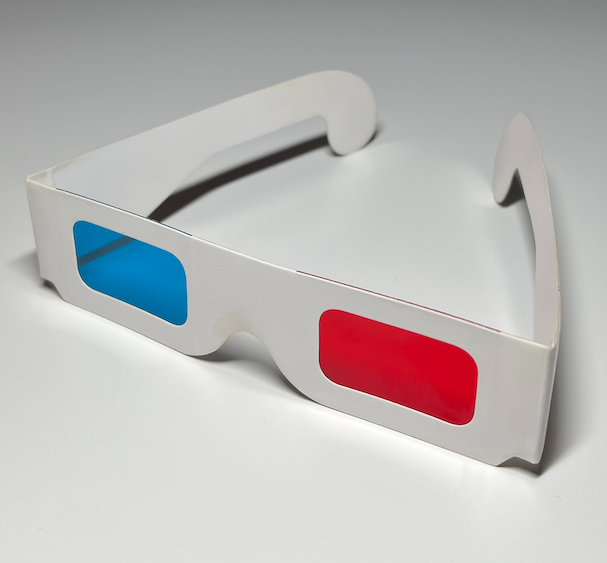

3D Glasses
|
3D glasses consist of a red lens for the left eye, and a cyan lens for the right eye. The color of an object is determined by which colors it absorbs. In the case of 3D glasses the red lens absorbs cyan, allowing only red to pass through — and that is why it is red. Similarly the cyan lens absorbs red, allowing only cyan to pass through — and that is why it is cyan.
An anaglyph is constructed using the red channel of the left image, and the cyan channel of the right image. When the anaglyph is viewed through the glasses the left eye only sees the red left image, and the right eye only sees the cyan right image. The brain then processes the left and right images, as it does for normal viewing, to give the illusion of depth.
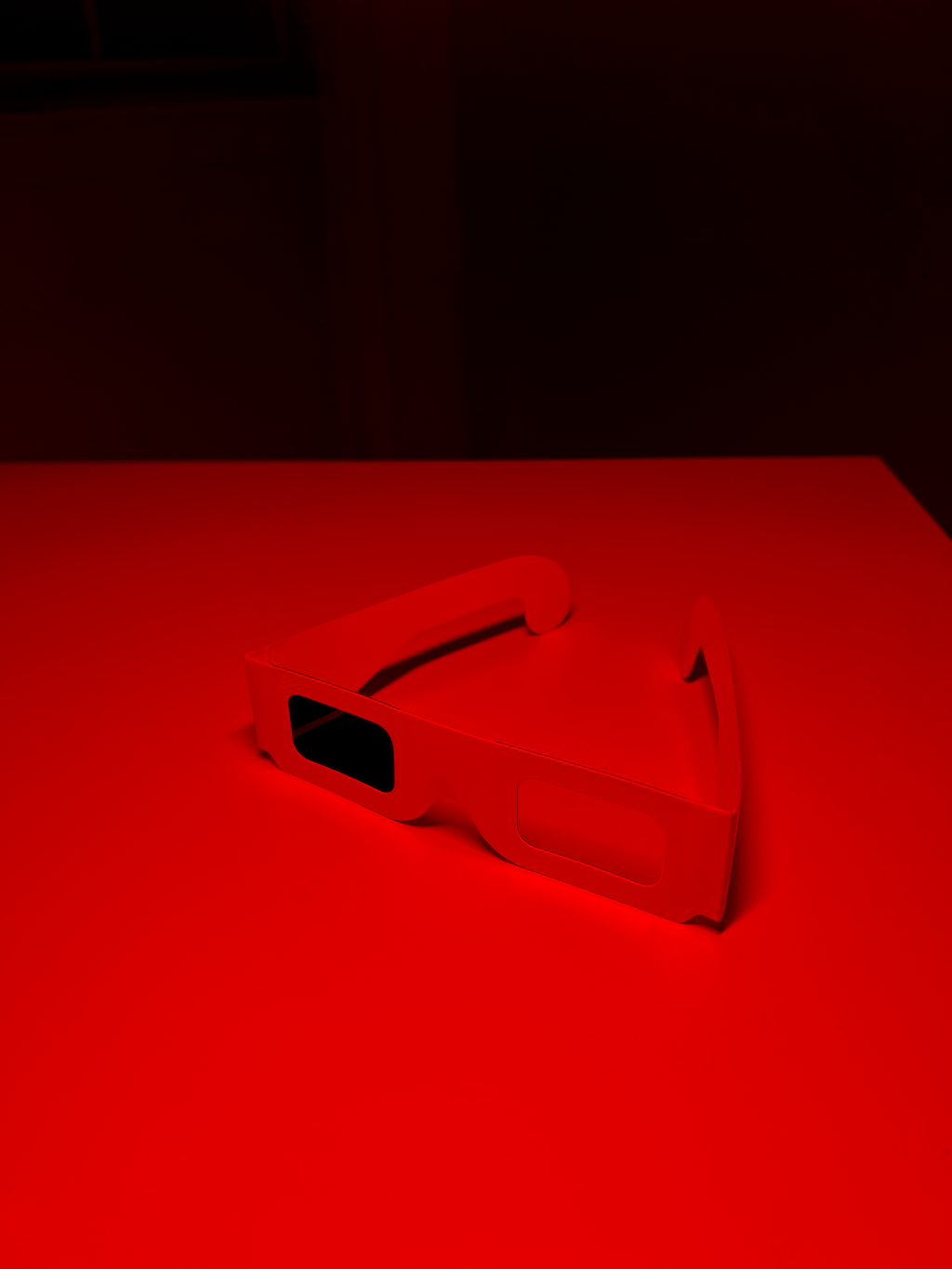
Left Eye
Red Channel
|
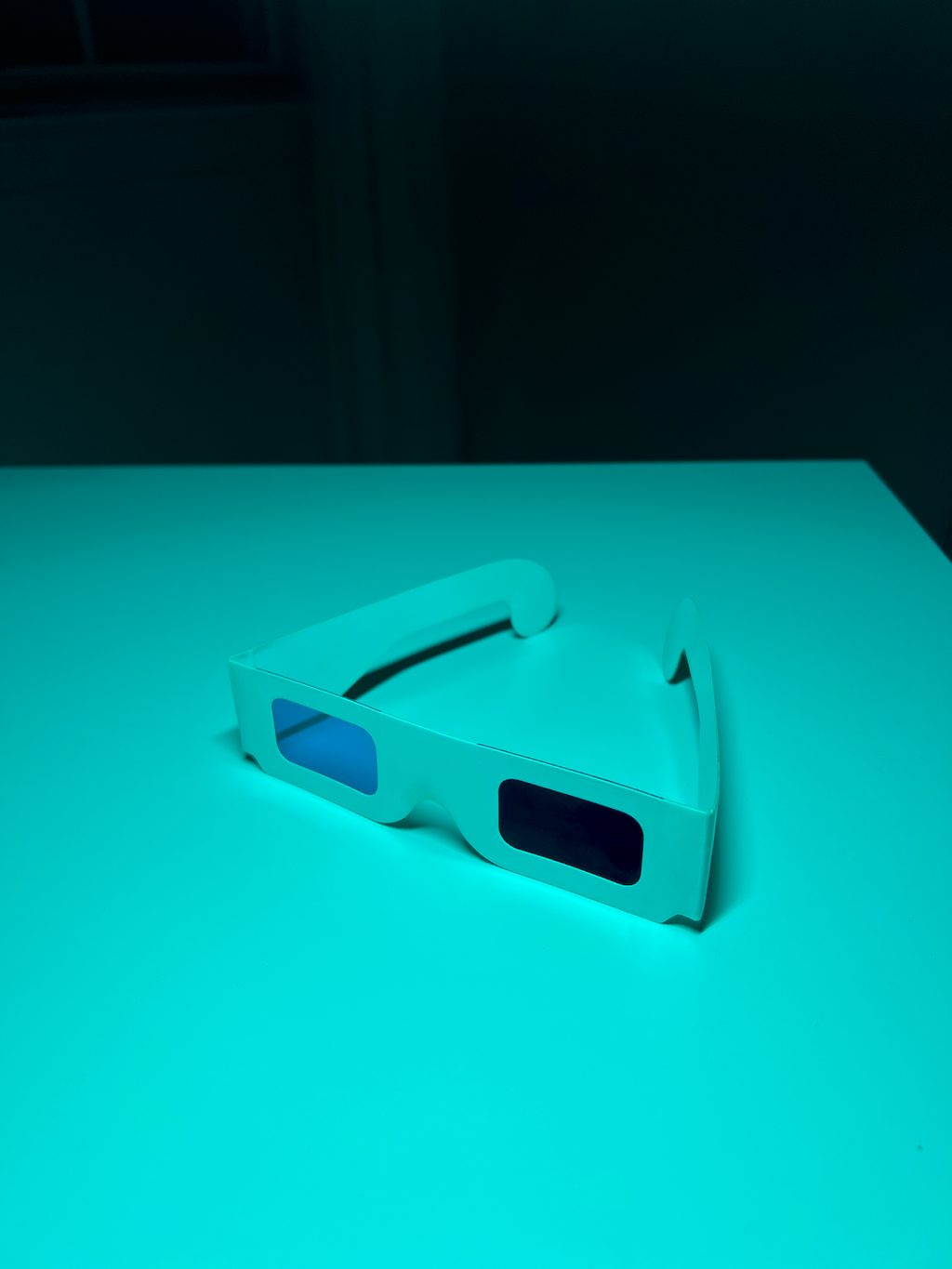
Right Eye
Green+Blue Channel
|

Anaglyph - All Channels
|
|
Taking Photos
- 1. Tap the Take Photos button to open the camera.
- 2. Capture two images — the second slightly to the right of the first — the app will present a cue and guide to aid in aligning the second shot with the first.
- 3. After capturing both images, the app will automatically create an anaglyph image.
- 4. Captured images appear below the Take Photos button. Retake photos by tapping the button again. Tap the image zoom button for a closer view. To save the anaglyph image, tap the save button. To save all images use the menu in the upper left side of the main veiw.
- 5. Repeat: Experiment with different right shift offsets. Save and compare.
Anaglyph Examples
Get your 3D glasses!
Example 1
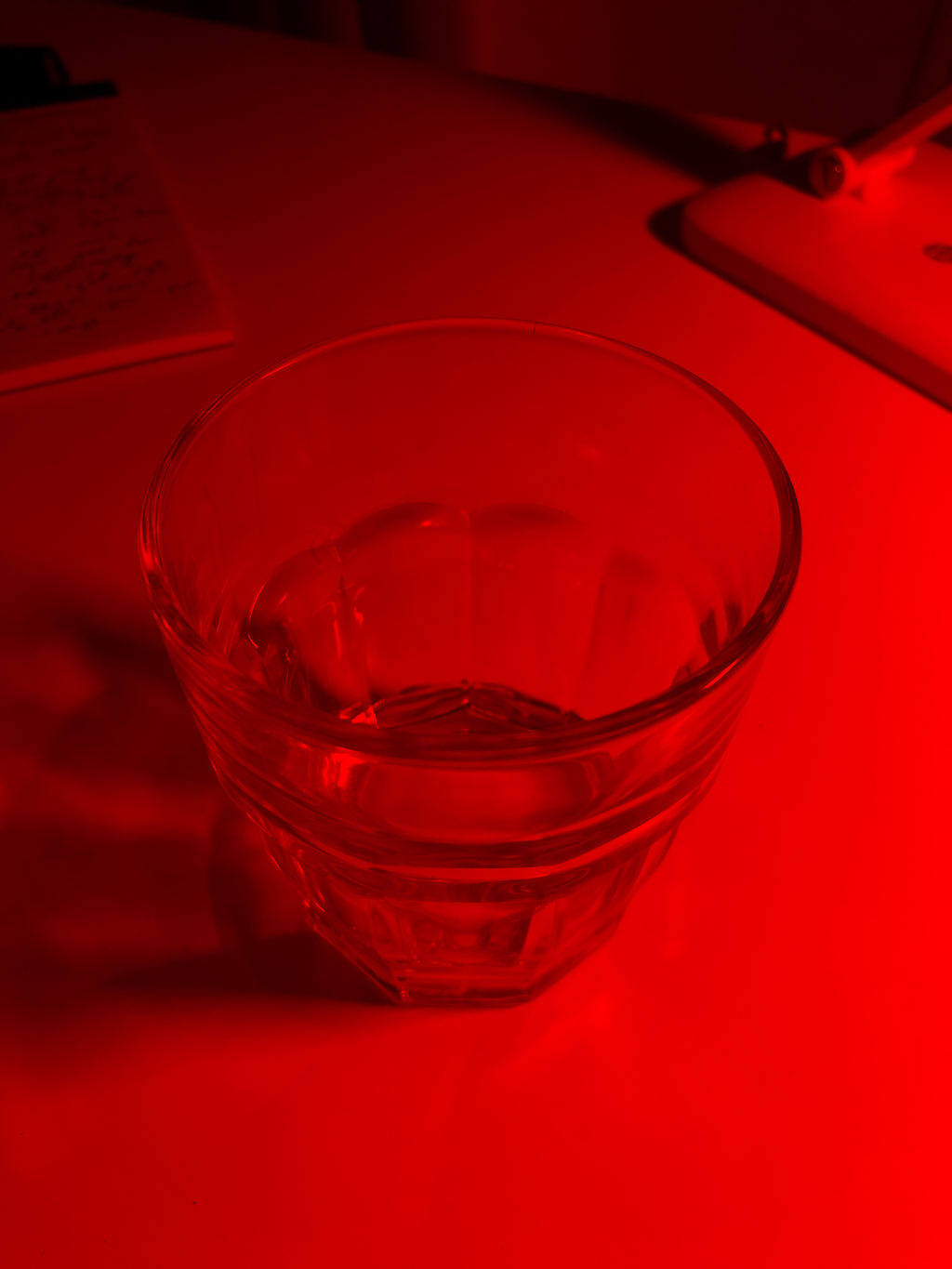

Left Eye
Red Channel
|
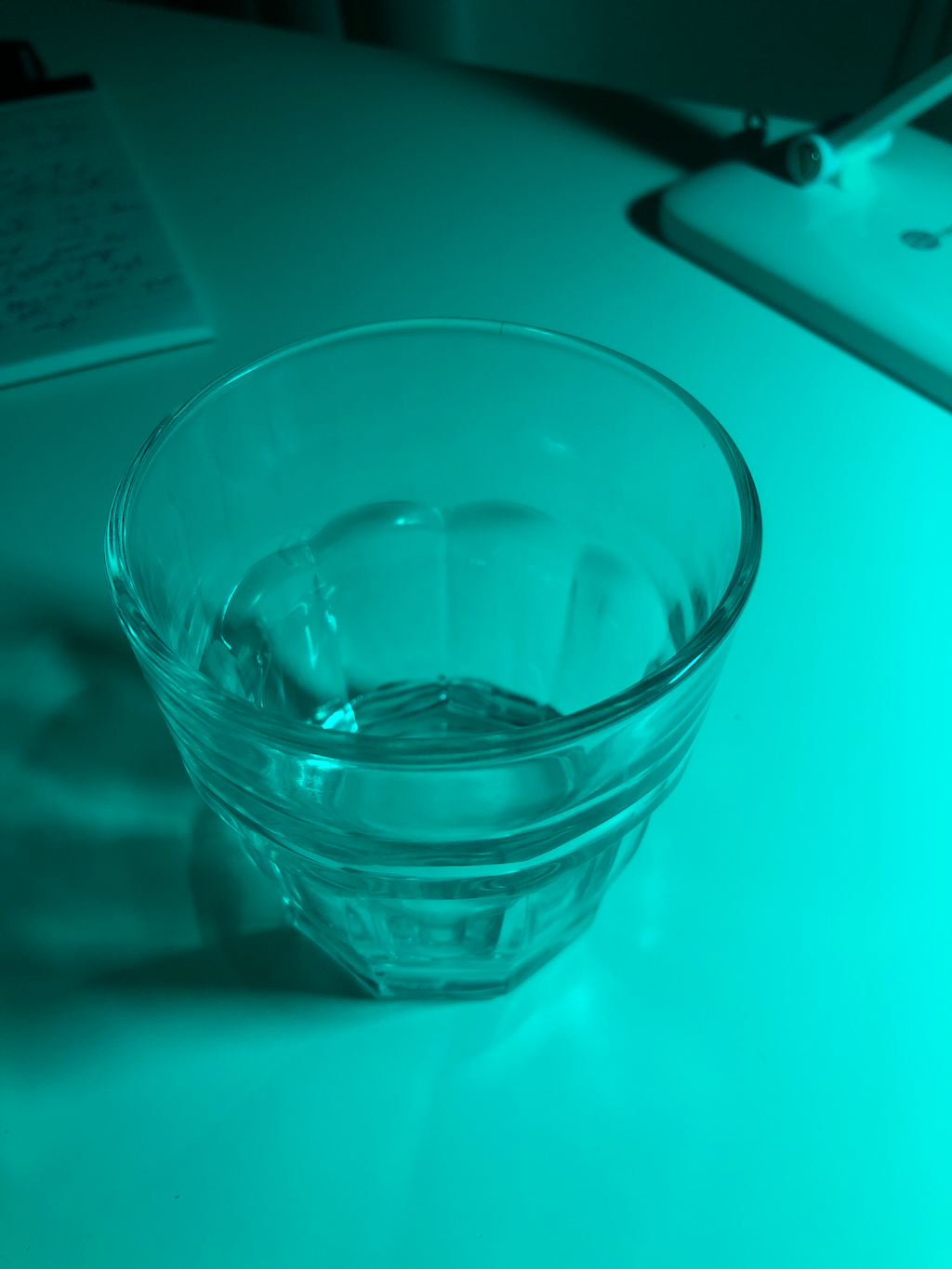

Right Eye
Green+Blue Channel
|

Anaglyph - All Channels
|
|
Example 2
Left Eye
Red Channel
|
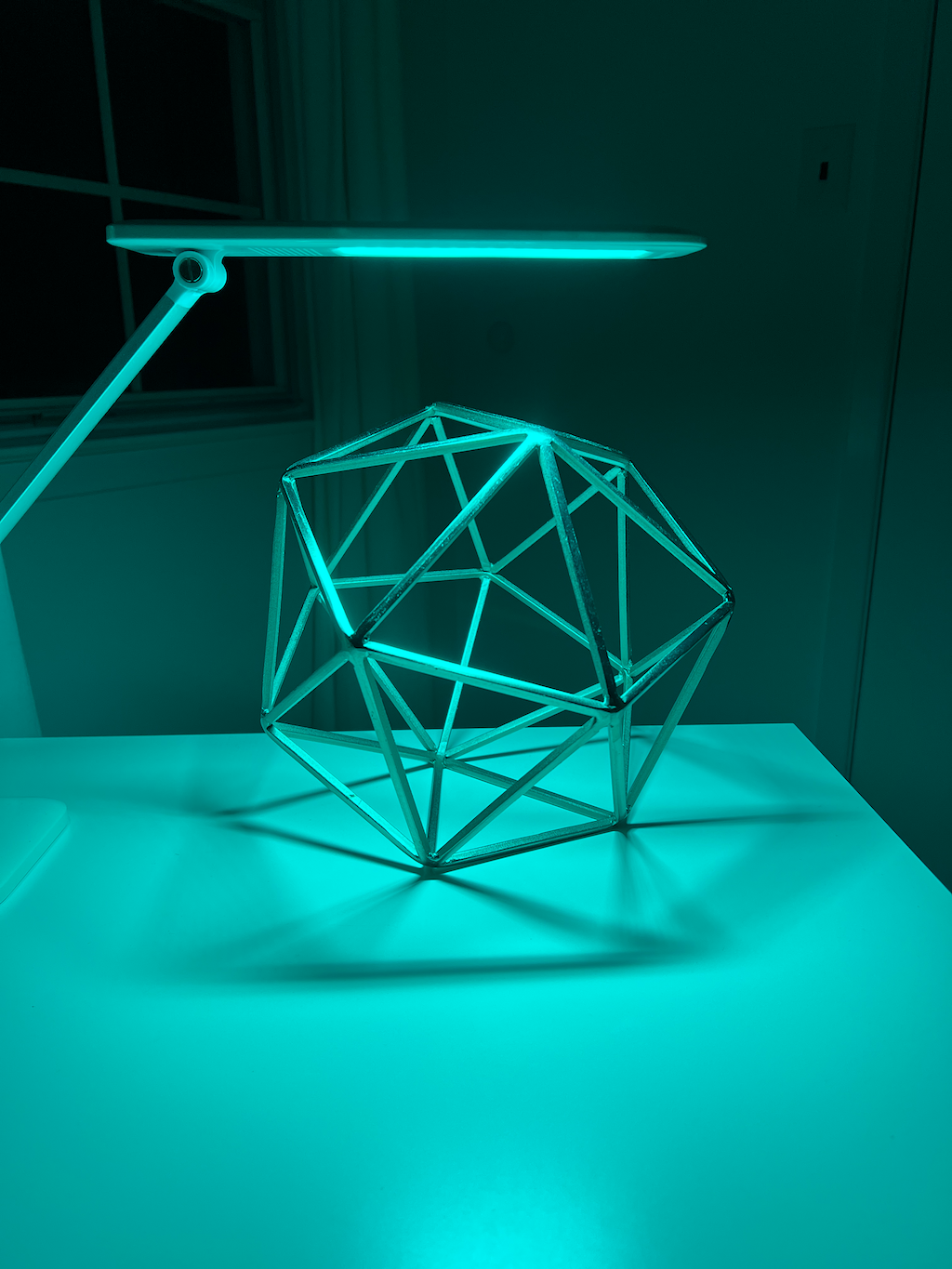

Right Eye
Green+Blue Channel
|

Anaglyph - All Channels
|
|
Some Tips
- Minimize Camera Tilt
Avoid tilting the camera up or down. The disparity should only be horizontal (side to side) for a natural depth effect.
- Keep the Camera at Eye Level
Align the camera with the subject at eye level for a more realistic perspective and depth effect.
- Capture the Same Scene
Ensure both images are of the same subject, taken from two slightly different viewpoints to achieve depth.
- Consider the Distance Between the Eyes
The distance between the two viewpoints should mimic the average distance between human eyes—about 6.5 cm (2.5 inches).
- Lighting Consistency
Ensure the lighting is consistent between the two images to maintain a natural 3D effect.
- Test and Review
Do some test shots and check the results to make sure the depth effect is right.
Practice and enjoy sharing anaglyphs!